by KeAi Communications Co.
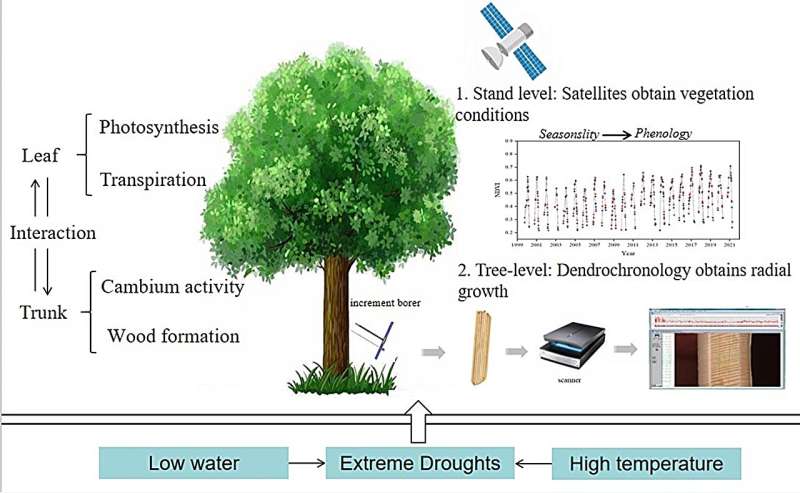
A recent study from China has shed light on the profound impacts of extreme droughts on forest ecosystems, particularly in water-limited regions. The findings revealed significant differences in how various tree species respond to such stressors.
Conducted in the Horqin Sandy Land of Northeast China, the research used dendrochronology and remote sensing techniques to examine the responses of both native maple-oak forests and introduced poplar plantations to extreme drought conditions. The study’s findings, published in the journal Forest Ecosystems, underscore the critical role of precipitation and the self-calibrated Palmer Drought Severity Index (scPDSI) in influencing tree growth and vegetation health.
The severe droughts experienced between 2000 and 2004 led to notable declines in radial growth and vegetation index (NDVI) across the studied tree species. The impact was particularly severe on the poplar species, with fast-growing poplar species showing more dramatic declines in growth rates and vegetation health than native maple and oak species. This indicates a species-specific trade-off between drought resilience and growth rate, with fast-growing species like poplar being more vulnerable to drought conditions.
Moreover, the study discovered that while radial growth showed no significant correlation with scPDSI, NDVI demonstrated a significant positive correlation, highlighting the greater sensitivity of canopy performance to drought stress than on the scale of inter-annual events radial growth.
These insights are crucial for forest management and afforestation efforts, especially in the context of climate change. Understanding species-specific responses to extreme droughts can guide the selection of tree species that are better suited to withstand water-limited conditions, ensuring the sustainability and resilience of forest ecosystems.
More information:
Han Shi et al, Resilience and response: Unveiling the impacts of extreme droughts on forests through integrated dendrochronological and remote sensing analyses, Forest Ecosystems (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.fecs.2024.100209. www.sciencedirect.com/science/ … 2197562024000459?via%3Dihub
Provided by
KeAi Communications Co.
Citation:
Impacts of extreme drought on forest ecosystems reveal species-specific adaptation differences in Northeast China (2024, July 12)
retrieved 13 July 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-07-impacts-extreme-drought-forest-ecosystems.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

