New results from the first archaeological fieldwork conducted in space show the International Space Station is a rich cultural landscape where crew create their own “gravity” to replace Earth’s, and adapt module spaces to suit their needs.
Archaeology is usually thought of as the study of the distant past, but it’s ideally suited for revealing how people adapt to long-duration spaceflight.
In the SQuARE experiment described in our new paper in PLOS ONE, we re-imagined a standard archaeological method for use in space, and got astronauts to carry it out for us.
Archaeology … in … spaaaaace!
The International Space Station is the first permanent human settlement in space. Close to 280 people have visited it in the past 23 years.
Our team has studied displays of photos, religious icons and artworks made by crew members from different countries, observed the cargo that is returned to Earth, and used NASA’s historic photo archive to examine the relationships between crew members who serve together.
We’ve also studied the simple technologies, such as Velcro and resealable plastic bags, which astronauts use to recreate the Earthly effect of gravity in the microgravity environment—to keep things where you left them, so they don’t float away.
Most recently, we collected data about how crew used objects inside the space station by adapting one of the most traditional archaeological techniques, the “shovel test pit.”
On Earth, after an archaeological site has been identified, a grid of one-meter squares is laid out, and some of these are excavated as “test pits.” These samples give a sense of the site as a whole.
In January 2022, we asked the space station crew to lay out five roughly square sample areas. We chose the square locations to encompass zones of work, science, exercise and leisure. The crew also selected a sixth area based on their own idea of what might be interesting to observe. Our study was sponsored by the International Space Station National Laboratory.
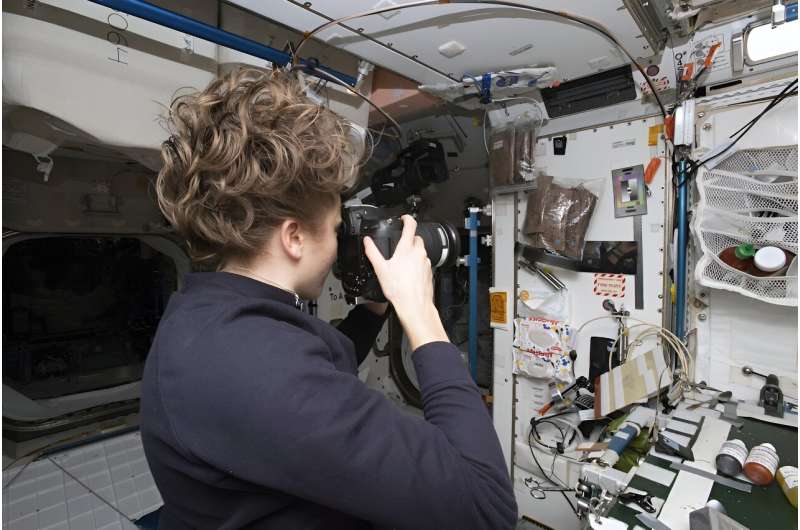

Then, for 60 days, the crew photographed each square every day to document the objects within its boundaries. Everything in space culture has an acronym, so we called this activity the Sampling Quadrangle Assemblages Research Experiment, or SQuARE.
The resulting photos show the richness of the space station’s cultural landscape, while also revealing how far life in space is from images of sci-fi imagination.
The space station is cluttered and chaotic, cramped and dirty. There are no boundaries between where the crew works and where they rest. There is little to no privacy. There isn’t even a shower.
What we saw in the squares
Now we can present results from the analysis of the first two squares. One was located in the US Node 2 module, where there are four crew berths, and connections to the European and Japanese labs. Visiting spacecraft often dock here. Our target was a wall where the Maintenance Work Area, or MWA, is located. There’s a blue metal panel with 40 velcro squares on it, and a table below for fixing equipment or doing experiments.
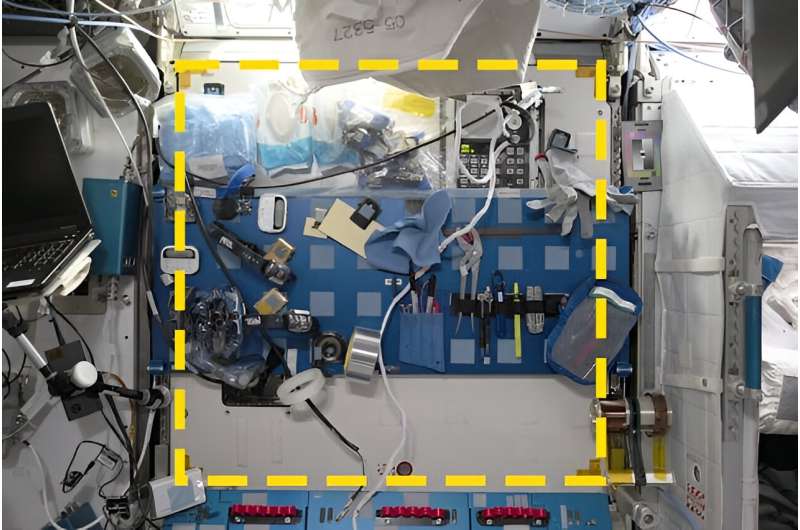
NASA intended the area to be used for maintenance. However, we saw hardly any evidence of maintenance there, and only a handful of science activities. In fact, for 50 of the 60 days covered by our survey, the square was only used for storing items, which may not even have been used there.
The amount of velcro here made it a perfect location for ad hoc storage. Close to half of all items recorded (44%) were related to holding other items in place.
The other square we’ve completed was in the US Node 3 module, where there are exercise machines and the toilet. It’s also a passageway to the crew’s favorite part of the space station, the seven-sided cupola window, and to storage modules.
This wall had no designated function, so it was used for eclectic purposes, such as storing a laptop, an antibacterial experiment and resealable bags. And for 52 days during SQuARE, it was also the location where one crew member kept their toiletry kit.
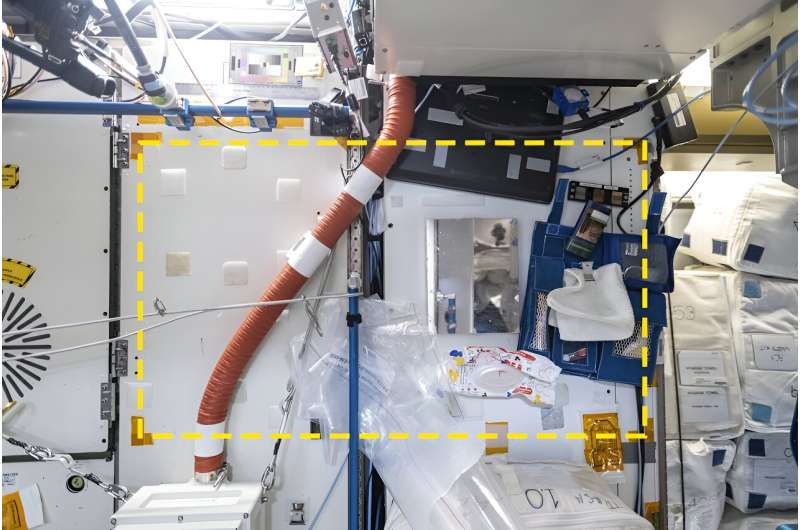

It makes a kind of sense to put one’s toiletries near the toilet and the exercise machines that each astronaut uses for hours every day. But this is a highly public space, where others are constantly passing by. The placement of the toiletry kit shows how inadequate the facilities are for hygiene and privacy.
What does this mean?
Our analysis of Squares 03 and 05 helped us understand how restraints such as velcro create a sort of transient gravity.
Restraints used to hold an object form a patch of active gravity, while those not in use represent potential gravity. The artifact analysis shows us how much potential gravity is available at each location.
The main focus of the space station is scientific work. To make this happen, astronauts have to deploy large numbers of objects. Square 03 shows how they turned a surface intended for maintenance into a halfway house for various items on their journeys around the station.
Our data suggests that designers of future space stations, such as the commercial ones currently planned for low Earth orbit, or the Gateway station being built for lunar orbit, might need to make storage a higher priority.
Square 05 shows how a public wall space was claimed for personal storage by an unknown crew member. We already know there is less-than-ideal provision for privacy, but the persistence of the toiletry bag at this location shows how crew adapt spaces to make up for this.
What makes our conclusions significant is that they are evidence-based. The analysis of the first two squares suggests the data from all six will offer further insights into humanity’s longest surviving space habitat.
Current plans are to bring the space station down from orbit in 2031, so this experiment may be the only chance we have to gather archaeological data.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()
Citation:
Archaeologists conduct first ‘space excavation’ on ISS and discover surprising quirks of zero-G life (2024, August 10)
retrieved 10 August 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-08-archaeologists-space-excavation-iss-quirks.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

